|
基本信息Personal Information
副研究员(自然科学) 硕士生导师
性别 : 男
毕业院校 : 中国科学院大连化学物理研究所
学历 : 博士研究生毕业
学位 : 博士学位
在职信息 : 在岗
所在单位 : 杭州高等研究院
入职时间 : 2019年11月14日
办公地点 : 杭州高等研究院童趣楼101-2
联系方式 : 0571-82257902
Email :
20251006_双光束红外光谱研究Cu/SSZ上NH3-SCR反应机制的合作论文正式被Journal of Catalysis接收!
发布时间 : 2025-10-06 点击量 :
Click here: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021951725005391
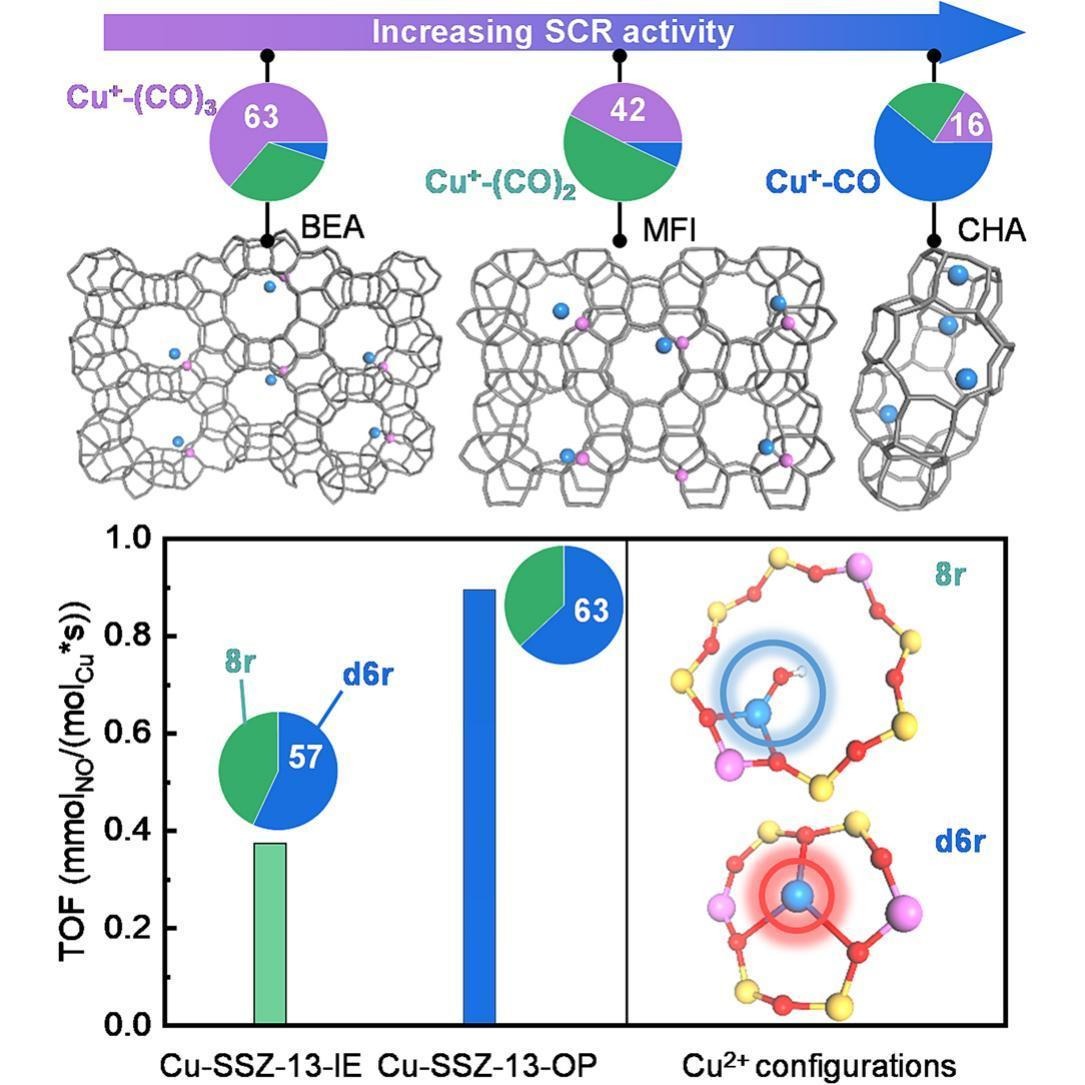
DB-FTIR Spectroscopy Unravels Confinement-Driven Modulation of Cu Species in Zeolite Catalysts for Low- Temperature NH3-SCR of NOx
Abstract
The confinement of active sites within zeolite frameworks critically governs the performance of Cu-based catalysts for low-temperature ammonia selective catalytic reduction (NH3-SCR) of NOx, but the mechanistic insights regarding the nature of active Cu species remain elusive. Here, we systematically elucidate the topology-driven modulation of Cu species by integrating advanced characterizations, including X-ray absorption spectroscopy, in situ dual-beam Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, low-temperature CO/NO adsorption, and catalytic evaluations across Cu-SSZ-13, Cu-ZSM-5, Cu-Beta, and oxide-supported analogues. We demonstrate that, i) in comparison to MFI and BEA topologies, the strong spatial confinement within the CHA framework preferentially forms most abundant Cu+ sites with low-coordination numbers to carbonyl species, and stabilizes Z2Cu2+ species in six-membered rings, enhancing Cu+/Cu2+ redox cycle and thus NO adsorption and nitrate turnover efficiency. ii) The ion-exchange and one-pot synthesis methods strongly influence the distribution and location Cu2+ species in Cu-SSZ-13 that further influence the activity. Mechanistic insights from in situ spectroscopy reveal that topology-governed Cu speciation dictates the formation and consumption of critical nitrate intermediates, enabling efficient low-temperature SCR cycles. These findings not only establish a clear topology-activity relationship for Cu-containing zeolite catalysts but also offer a mechanistic blueprint for the rational design of catalysts, advancing NOx abatement technologies to meet increasingly stringent emission regulations.